Abstract
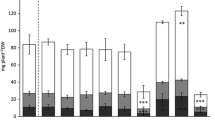
Cobalt is a minor contaminant in wetlands that has been linked to accumulation by Nyssa species for many years, though the evidence is largely anecdotal. We examined cobalt uptake characteristics from cobalt-enriched potting soil by Nyssa aquatica (water tupelo), N. sylvatica var. biflora (swamp tupelo), and Taxodium distichum (baldcypress), codominant canopy species of wetland forests of the southeastern United States. Seedlings were grown in 10 1 pots for two growing seasons. Cobalt additions (up to 100 mg/pot) did not affect biomass production of leaves, stems, or roots of the three species. Height was significantly different among treatments within a species, but no treatment was different from the control treatment with no added cobalt. Leaf cobalt concentrations were greater in N. sylvatica var. biflora than N. aquatica during the first year, but similar during the second year. Cobalt concentrations declined from the first to second years for T. distichum leaves. In the 100 mg/pot treatment, leaf cobalt concentrations of both Nyssa species during the second year were 150 times greater than that of T. distichum. Elevated cobalt uptake by Nyssa species is apparently a function of special mechanisms of the genera and not a habitat characteristic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Beeson, K. C., V. A. Lazar, and S. G. Boyce. 1955. Some plant accumulators of the micronutrient elements. Ecology 36: 155–56.
Brooks, R. R., J. A. McCleave, and E. K. Schofield. 1977. Cobalt and nickel uptake by the Nyssaceae. Taxon 26: 197–201.
Guthrie, R. K. and D. S. Cherry. 1979. The uptake of chemical elements from coal ash and settling basin effluent by primary producers. I. Relative concentrations in predominant plants. Science of the Total Environment 12: 217–22.
Kabata-Pendias, A. and H. Pendias. 2001. Trace elements in soils and plants, third edition. CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, FL, USA.
Kozlowski, T. T., P. J. Kramer, and S. G. Pallardy. 1991. The Physiology Ecology of Woody Plants. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA.
Kubota, J., V. A. Lazar, and K. C. Beeson. 1960. The study of cobalt status of soils in Arkansas and Louisiana using the black gum as the indicator plant. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings 24: 527–28.
McBride, M. B. 1994. Environmental Chemistry of Soils. Oxford University Press, New York, NY, USA.
McLeod, K. W. and T. G. Ciravolo. 2003. Sensitivity of water tupelo (Nyssa aquatica) and baldcypress (Taxodium distichum) seedlings to manganese-enrichment under water saturated conditions. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 22: 2948–51.
Robinson, B. H., R. R. Brooks, and M. J. Hedley. 1999. Cobalt and nickel accumulation in Nyssa (tupelo) species and its significance for New Zealand agriculture. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research 42: 235–40.
SAS Institute Inc. 1990. SAS Procedures Guide, Version 6, third edition. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA.
Steel, R. and J. Torrie. 1960. Principles and Procedures of Statistics. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, NY, USA.
Thomas, W. A. 1975. Cobalt accumulation and circulation by blackgum trees. Forest Science 21: 222–26.
Wallace, A., E. M. Romney, D. C. Adriano, J. Kinnear, and G. V. Alexander. 1982. Sources of variation in mineral composition of selected plants inhabiting a floodplain at the Savannah River Site. Soil Science 134: 36–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McLeod, K.W., Ciravolo, T.G. Cobalt uptake by Nyssa aquatica, N. sylvatica var. biflora, and Taxodium distichum seedlings. Wetlands 27, 40–43 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1672/0277-5212(2007)27[40:CUBNAN]2.0.CO;2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1672/0277-5212(2007)27[40:CUBNAN]2.0.CO;2